THIS ARTICLE WILL BE MODIFIED ACCORDINGLY
AT PRESENT ITS INCORRECT
AKSHAY DEORAS
Glossary-
*1] Electric charged particle- A particle having an electric charge ( Can be Negative charge or a positive charge)*2] Acceleration- Rate of change of velocity over a period of time. In one dimension it is rate of changes in speed of a body.*3] Accelerating electric charged particle- A particle having an electric charge (greater than 0C) which is in acceleration due to action of a certain force*4] Point charge- A point having a charge. For consideration, the point is taken as a sphere having a well defined diameter* Point otherwise its a dimension less quantity*5] Test charge- A ideal charge having magnitude,m (m~ 0)*6] Electric field- A well defined area around a charge where there is influence of chargeor area around a point charge where force from point charge are activeIn this case, area around an electric charge is called electric field*7] Electric field shape- Shape of the electric field(FOR THIS ARTICLE, THE SHAPE IS CONSIDERED ON A 2-DIMENSION)*8] Electric Field Intensity (Electric intensity)- Is the force experienced by a test charge having certain magnitude ( greater than 0) which is kept in electric field of a point chargeα- direct proportionality symbol
1] VARYING ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY FOR A POINT AND TEST CHARGE AT DIFFERENT STATESBasic-We consider a point charge P kept in vacuum at rest with a test charge Q at restPoint charge having magnitude equal to 20C.(Coulomb). Electric field intensity = F/qi.eVector E= Vector F/qwhere E and F vector and vectors of electric field and force respectively and q is the charge of Pconsidering magnitudes-E=F/q ....................... (1)
F= Ma .........................(2)where M is mass and a is acceleration of point charge whose force will be experienced by test charge kept in electric field
Putting value of eq.(2) in (1)
E= Ma/q ......................(3)
So Electric field intensity of a test charge at rest in vacuum is given by eq.(3) whereE α MaEα 1/q
Condition-Now we accelerate the point charge P by providing a Force(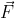 )having magnitude equal to 10N and direction along unit vector (
)having magnitude equal to 10N and direction along unit vector ( ) Let the mass of point charge be 1g and determined acceleration be 10m/s^
) Let the mass of point charge be 1g and determined acceleration be 10m/s^
Putting values in .. eq(3) and considering vector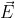 = 1*10/20 (
= 1*10/20 ( )
)
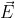 = 1/2 N/C (
= 1/2 N/C ( )
) 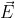 = 0.5N/C (
= 0.5N/C ( )..............(4)
)..............(4)
IN FIRST CASE WHERE THE POINT CHARGE WAS IN REST we get following result from .... eq(3)
E= Ma/q ......................(3)Where M=1g a= 0m/s^ q=20C
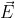 = 1*0/20 (
= 1*0/20 ( )where (
)where ( ) is unit vector along Force vector and accordingly for
) is unit vector along Force vector and accordingly for 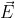 =0 (
=0 ( ) ...................(5) =0
) ...................(5) =0
On comparison of eq (4) and (5) we determine that there is a varying electric field intensity 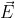 for a stationary point charge and test charge and a accelerating point charge and stationary test charge.*When the point charge is in a state of motion(increasing magnitude) then electric field intensity on stationary test charge increases in other words as distance between them decreases. * When point charge is stationary and test charge also then there is no net electric field intensity on a test charge
for a stationary point charge and test charge and a accelerating point charge and stationary test charge.*When the point charge is in a state of motion(increasing magnitude) then electric field intensity on stationary test charge increases in other words as distance between them decreases. * When point charge is stationary and test charge also then there is no net electric field intensity on a test charge
(II} VARYING ELECTRIC FIELD SHAPE. TO BE COMPLETED!
Glossary-
*1] Electric charged particle- A particle having an electric charge ( Can be Negative charge or a positive charge)
*2] Acceleration- Rate of change of velocity over a period of time. In one dimension it is rate of changes in speed of a body.
*3] Accelerating electric charged particle- A particle having an electric charge (greater than 0C) which is in acceleration due to action of a certain force
*4] Point charge- A point having a charge. For consideration, the point is taken as a sphere having a well defined diameter
* Point otherwise its a dimension less quantity
*5] Test charge- A ideal charge having magnitude,m (m~ 0)
*6] Electric field- A well defined area around a charge where there is influence of charge
or area around a point charge where force from point charge are active
In this case, area around an electric charge is called electric field
*7] Electric field shape- Shape of the electric field
(FOR THIS ARTICLE, THE SHAPE IS CONSIDERED ON A 2-DIMENSION)
*8] Electric Field Intensity (Electric intensity)-
Is the force experienced by a test charge having certain magnitude ( greater than 0) which is kept in electric field of a point charge
α- direct proportionality symbol
1] VARYING ELECTRIC FIELD INTENSITY FOR A POINT AND TEST CHARGE AT DIFFERENT STATES
Basic-
We consider a point charge P kept in vacuum at rest with a test charge Q at rest
Point charge having magnitude equal to 20C.(Coulomb). Electric field intensity = F/q
i.e
Vector E= Vector F/q
where E and F vector and vectors of electric field and force respectively and q is the charge of P
considering magnitudes-
E=F/q ....................... (1)
F= Ma .........................(2)
where M is mass and a is acceleration of point charge whose force will be experienced by test charge kept in electric field
Putting value of eq.(2) in (1)
E= Ma/q ......................(3)
So Electric field intensity of a test charge at rest in vacuum is given by eq.(3) where
E α Ma
Eα 1/q
Condition-
Now we accelerate the point charge P by providing a Force(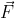 )
)
having magnitude equal to 10N and direction along unit vector
( )
)
Let the mass of point charge be 1g and determined acceleration be 10m/s^
Putting values in .. eq(3) and considering vector
IN FIRST CASE WHERE THE POINT CHARGE WAS IN REST we get following result from .... eq(3)